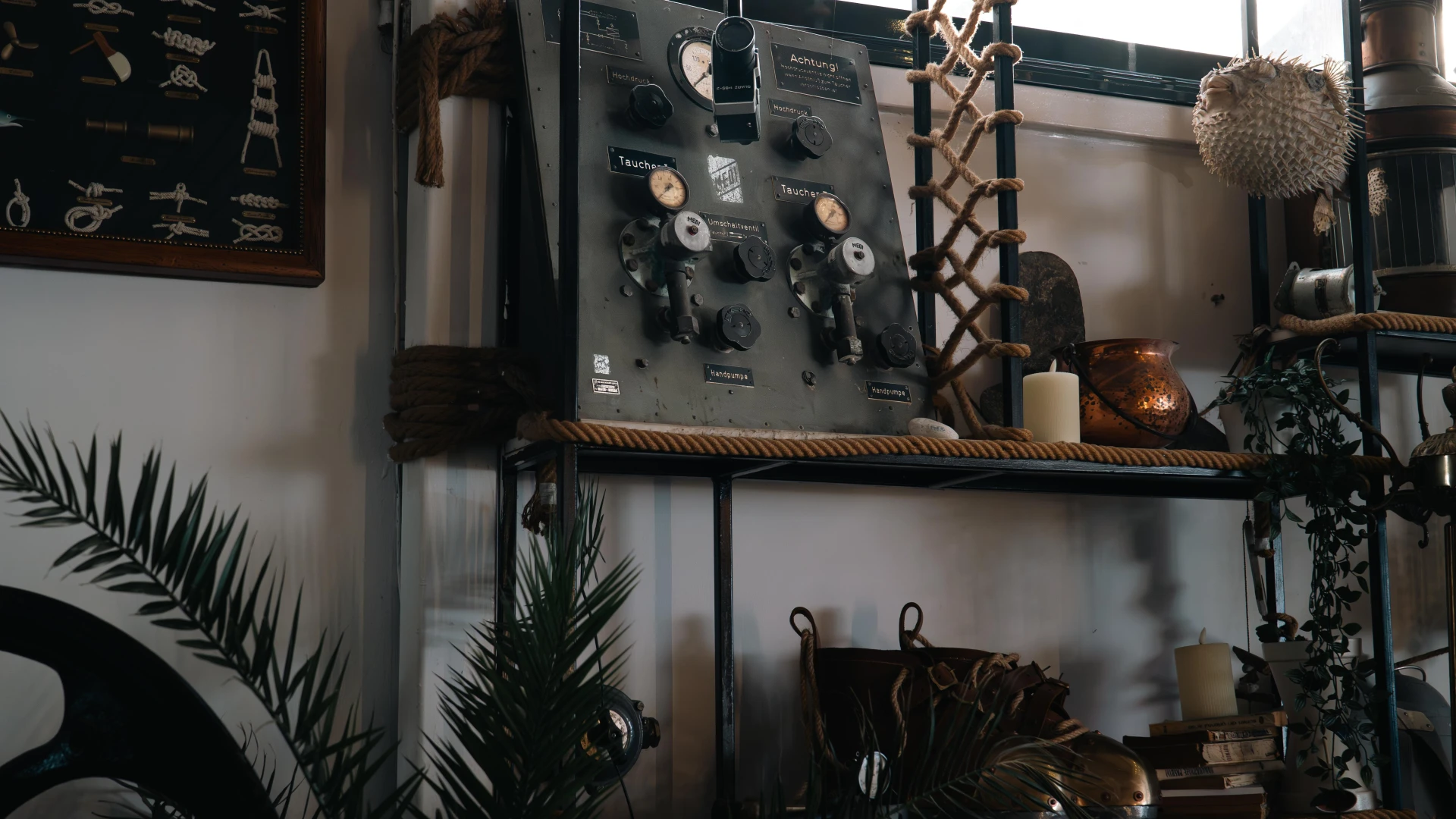
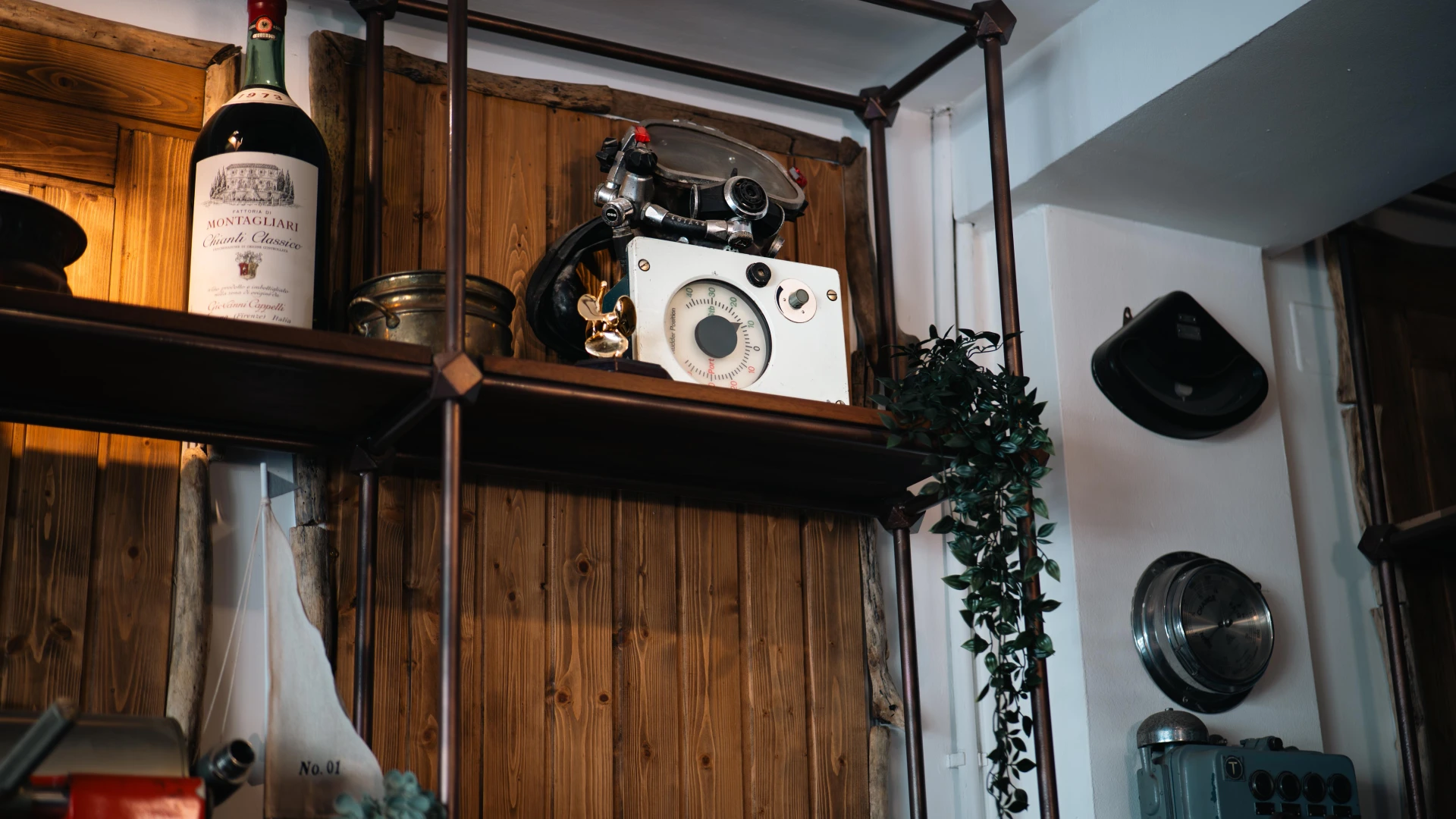
This manual air distribution panel, built in Germany 80 years ago, supplied two divers simultaneously from a single hand-operated air pump. Equipped with pressure gauges and adjustable valves, it was essential for surface-supplied diving, allowing precise air control. A rare and fascinating piece of historical diving technology.

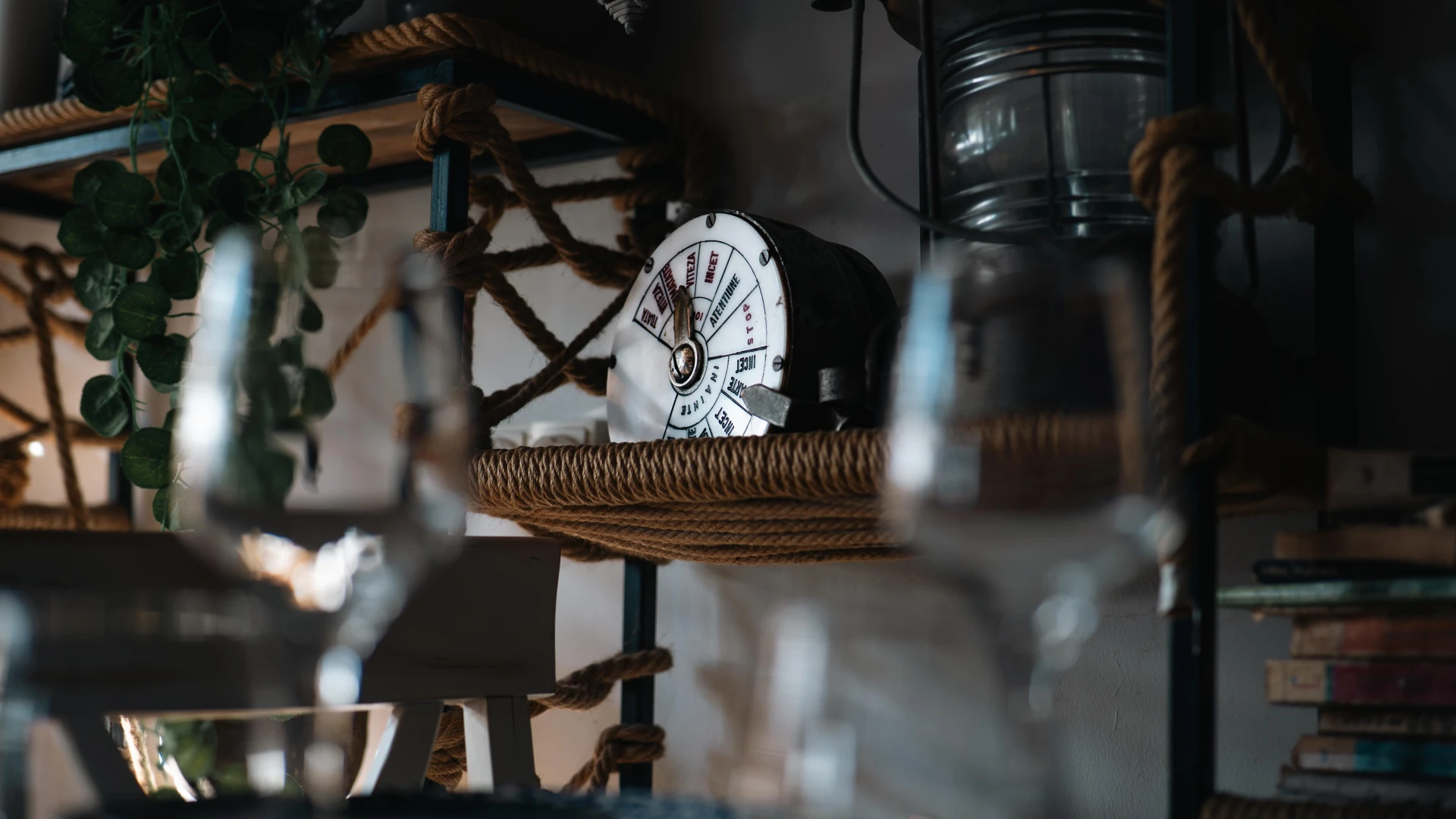
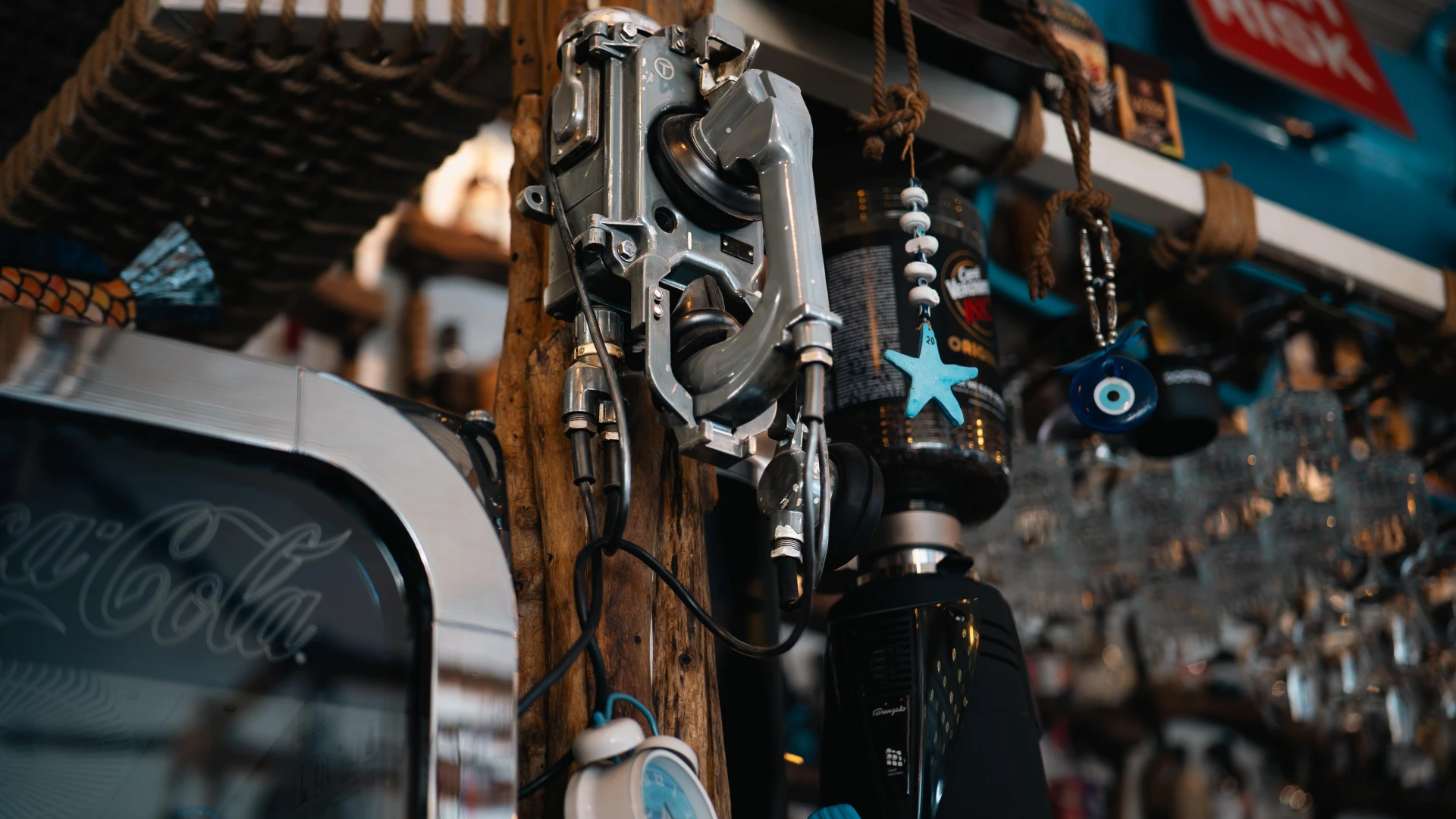
This engine order telegraph was a key component in navigational command aboard merchant and military vessels. Constructed from durable metal with an enameled panel, it facilitated communication between the bridge and engine room, ensuring precise speed and direction adjustments. A true testament to classic maritime engineering, this rare artifact recalls an era when manual operations demanded skill and accuracy from the crew.

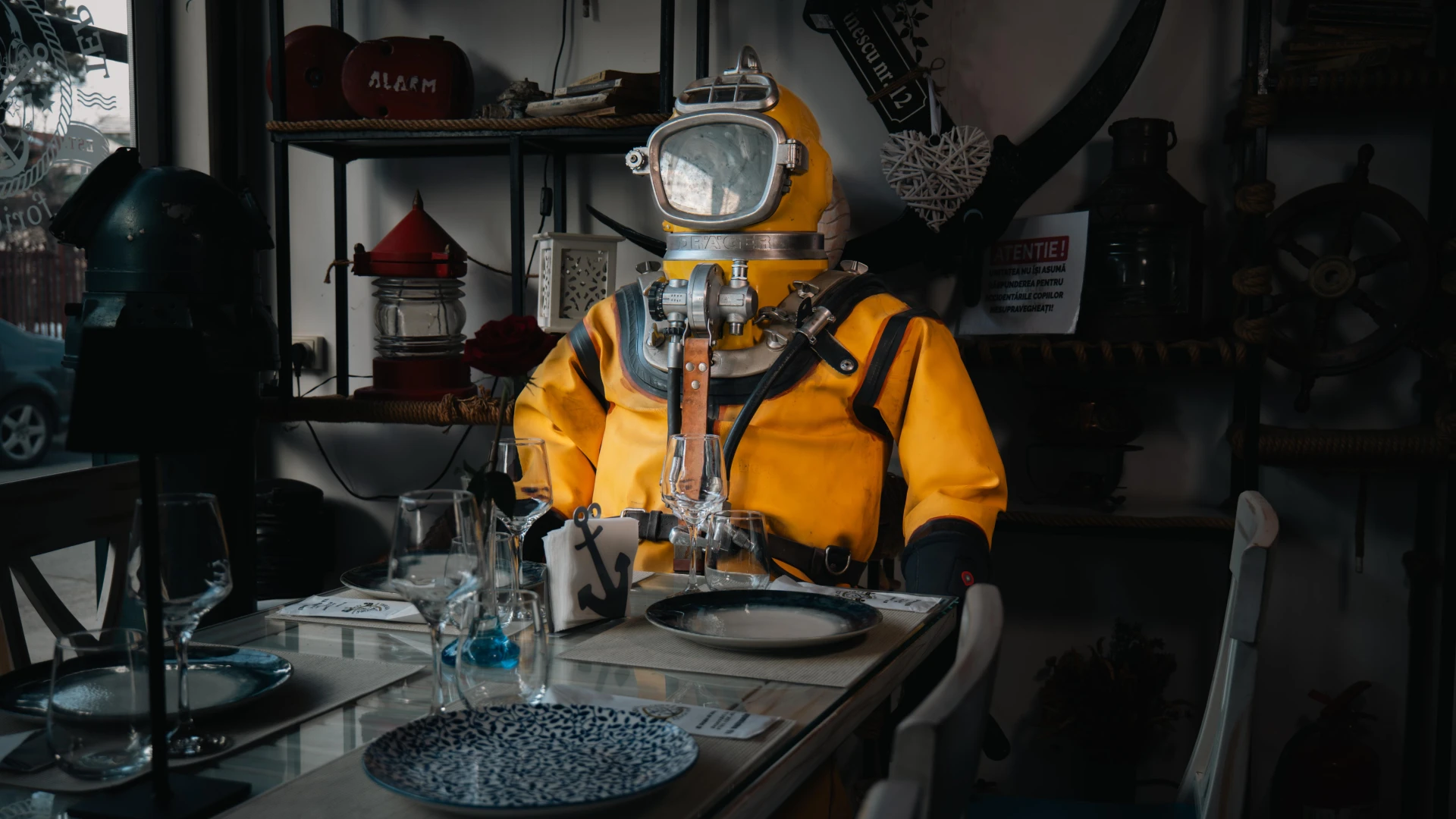
Designed for extreme missions, this Dräger heavy diving suit (1960-1970) was used for contaminated water operations and surface-supplied underwater work. Made from materials resistant to chemicals and biological hazards, this suit provided maximum protection and complete sealing. A true symbol of industrial diving, it played a crucial role in high-risk technical interventions, proving unmatched reliability and safety.

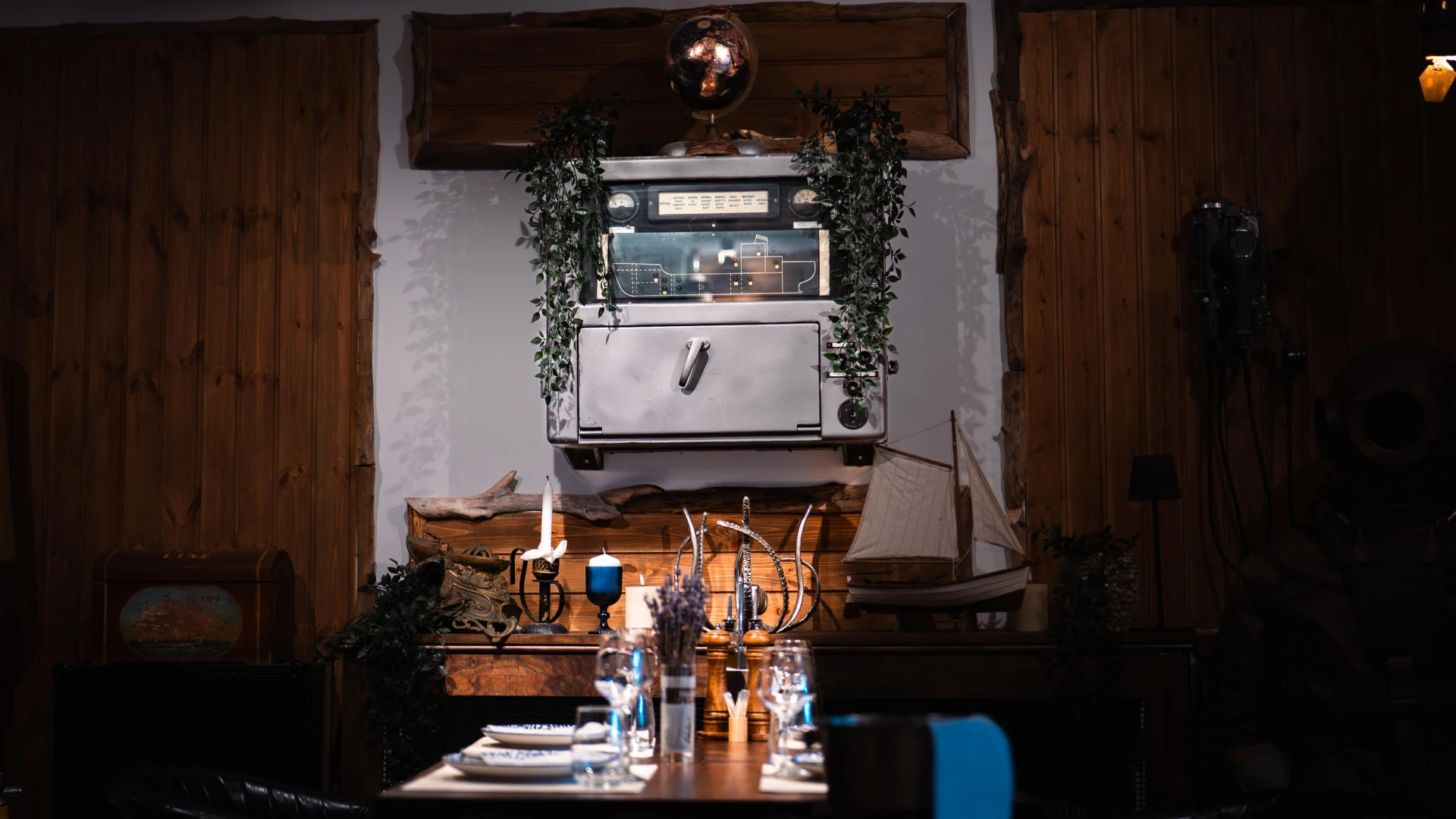
This Russian naval emergency panel was used for detecting and alerting the crew about hull breaches and structural damages. The system displayed affected areas and provided warnings for immediate action to prevent sinking. A crucial piece of maritime safety, now displayed at Terasa cu Ancore.

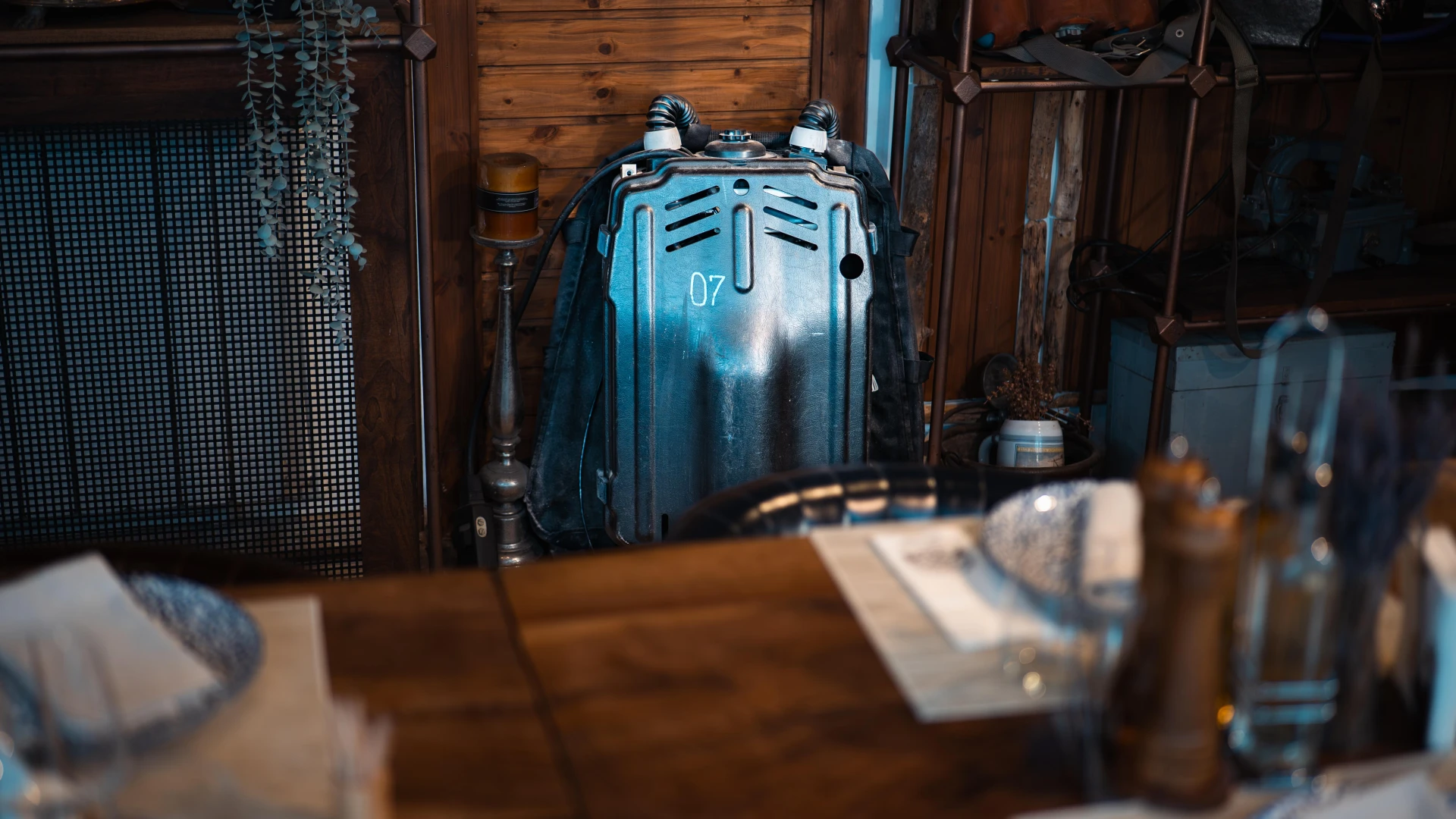
This SMT military diving apparatus is an amagnetic closed-circuit system used for covert underwater missions. It recycles exhaled gases, preventing bubbles and ensuring stealth operation. Designed for military divers, this elite equipment played a crucial role in special operations and deep-sea engineering tasks.

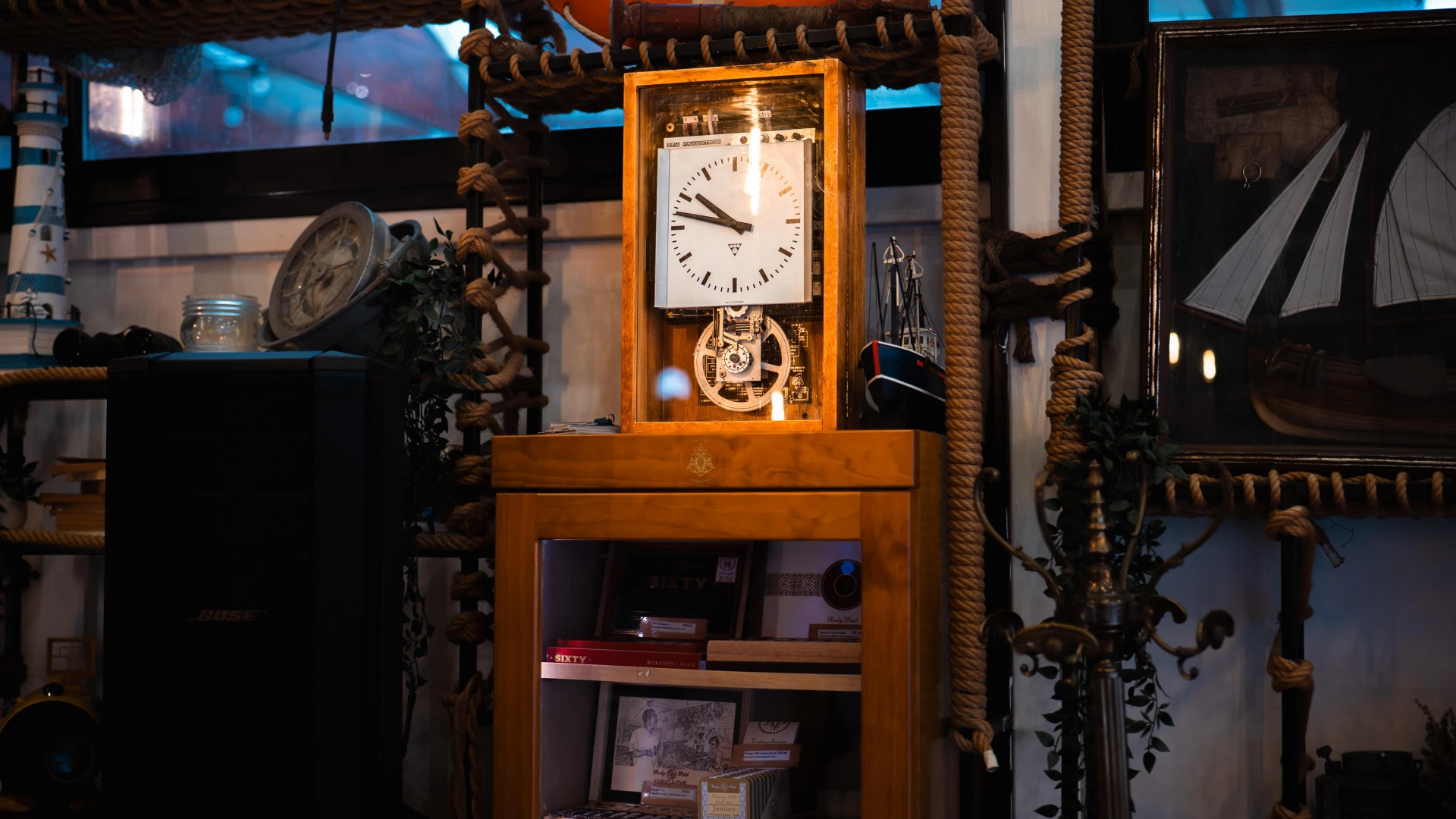
This Pragotron ship clock, manufactured in former Czechoslovakia, was used by a ship commander in the control room of a commercial vessel. The ZPA Pragotron model was known for its accuracy and was widely used in train stations, factories, and public institutions across Eastern Europe from the 1950s-60s. Its industrial design and robust mechanism showcase the reliability and technology of its era. A genuine maritime historical piece.

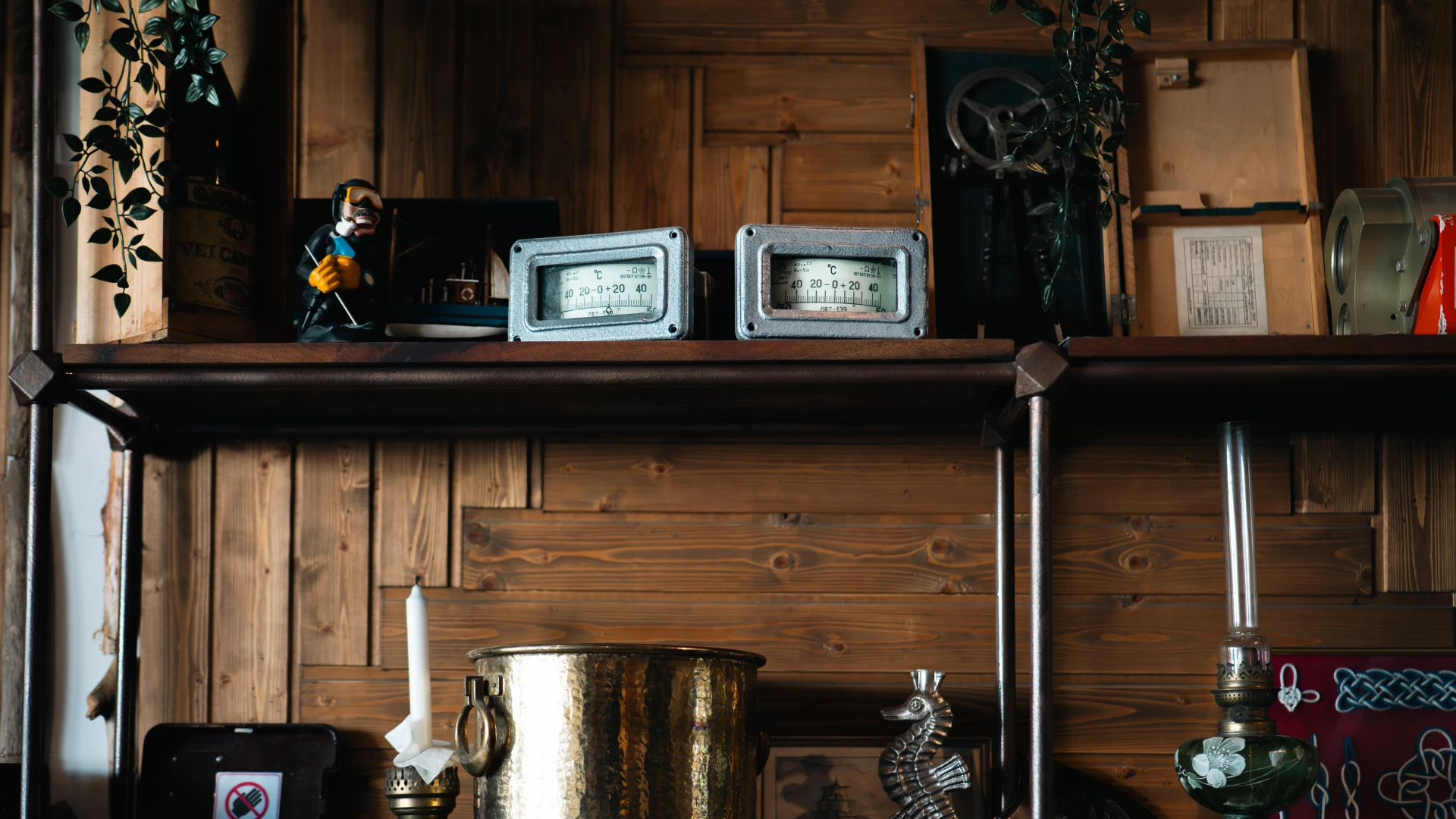
This marine inclinometer, used on commercial ships, accurately measures the vessel's tilt angle during navigation. Essential for maritime safety, it helps crews monitor ship stability and adjust cargo based on sea conditions. Built from durable materials, the inclinometer remains a standard instrument in the maritime industry. This historical model, once crucial for global navigation, is now displayed at Terasa cu Ancore.

This professional diving mask, used in technical underwater operations, ensured controlled breathing and safety for divers in extreme environments. Featuring adjustable valves, it allowed optimal air regulation, crucial for subsea missions. Alongside it, a rudder position indicator, a vital navigation tool, helped commercial ship crews monitor and adjust the ship's direction with high precision. These historical maritime artifacts are now displayed at Terasa cu Ancore.

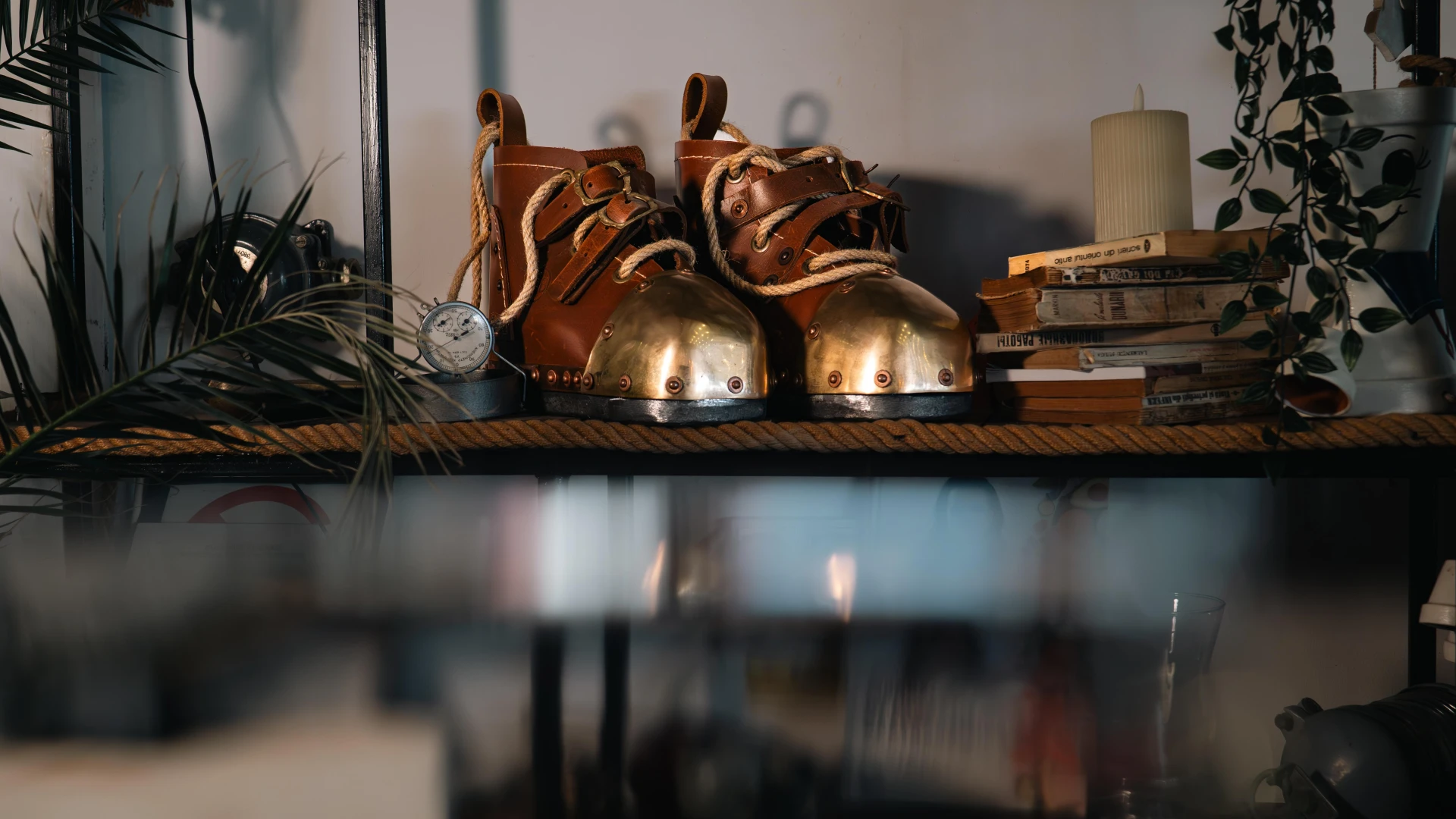
These heavy diving boots, an English model crafted from leather, bronze, and lead, were essential for professional divers, ensuring stability on the ocean floor. Weighing 10 kg per boot, they were a vital part of historical deep-sea diving gear, used in maritime operations and underwater engineering. A remarkable relic of classic diving history.

This is the first lifeboat radio, a crucial device used on rescue boats to send emergency signals. Designed with a floating case, it ensured effective communication with ships or rescue teams in distress situations. The Lifeboat Radio Class 1 marked a significant advancement in maritime safety, providing a lifeline for crews facing shipwrecks.

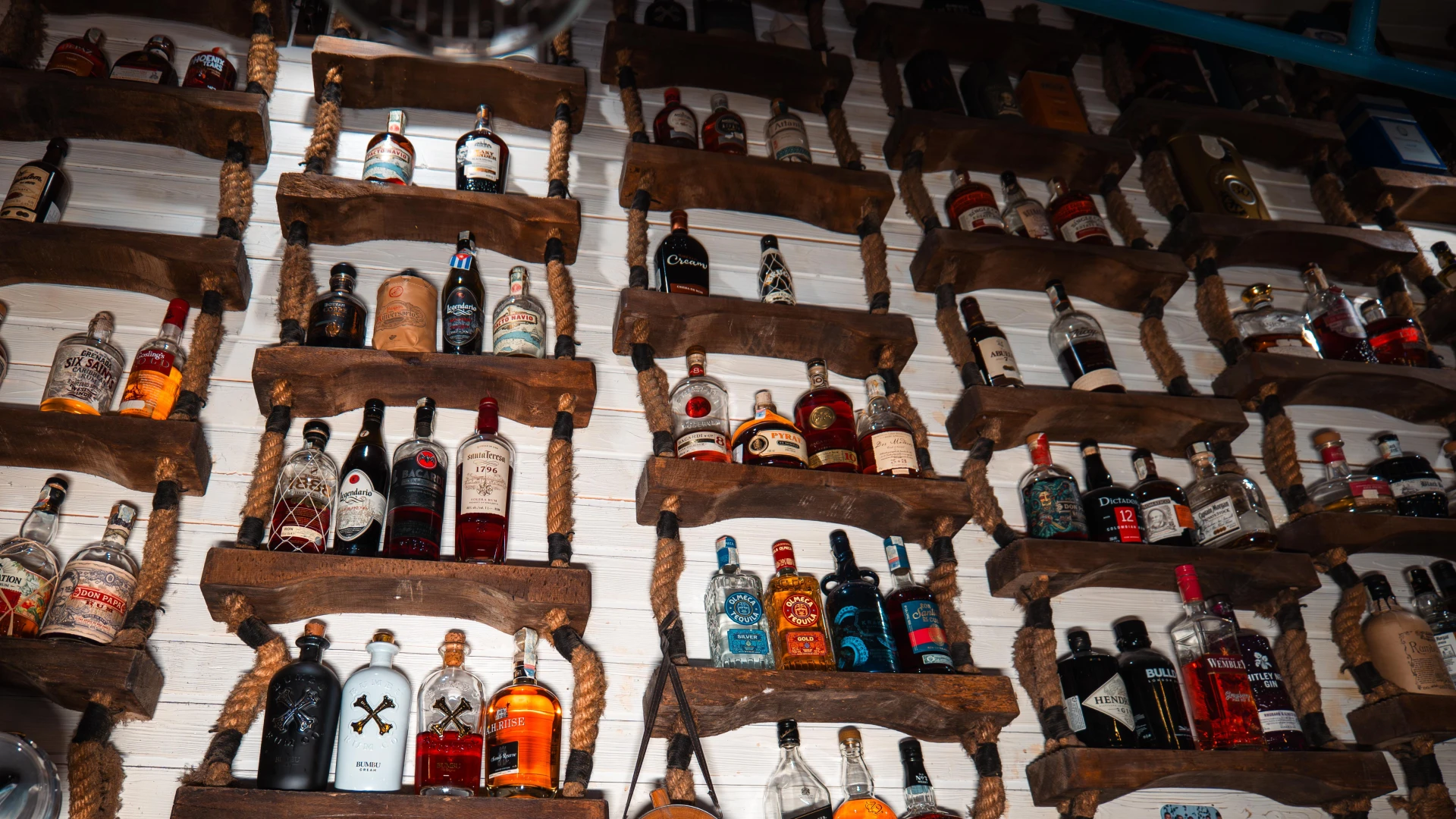
A maritime pilot ladder, known as a Pilot Ladder, has been transformed into a stunning display showcasing over 120 varieties of rum. This authentic nautical piece, once used for boarding ships, is now an iconic design element at Terasa cu Ancore. A true symbol of maritime adventure and exotic refinement.

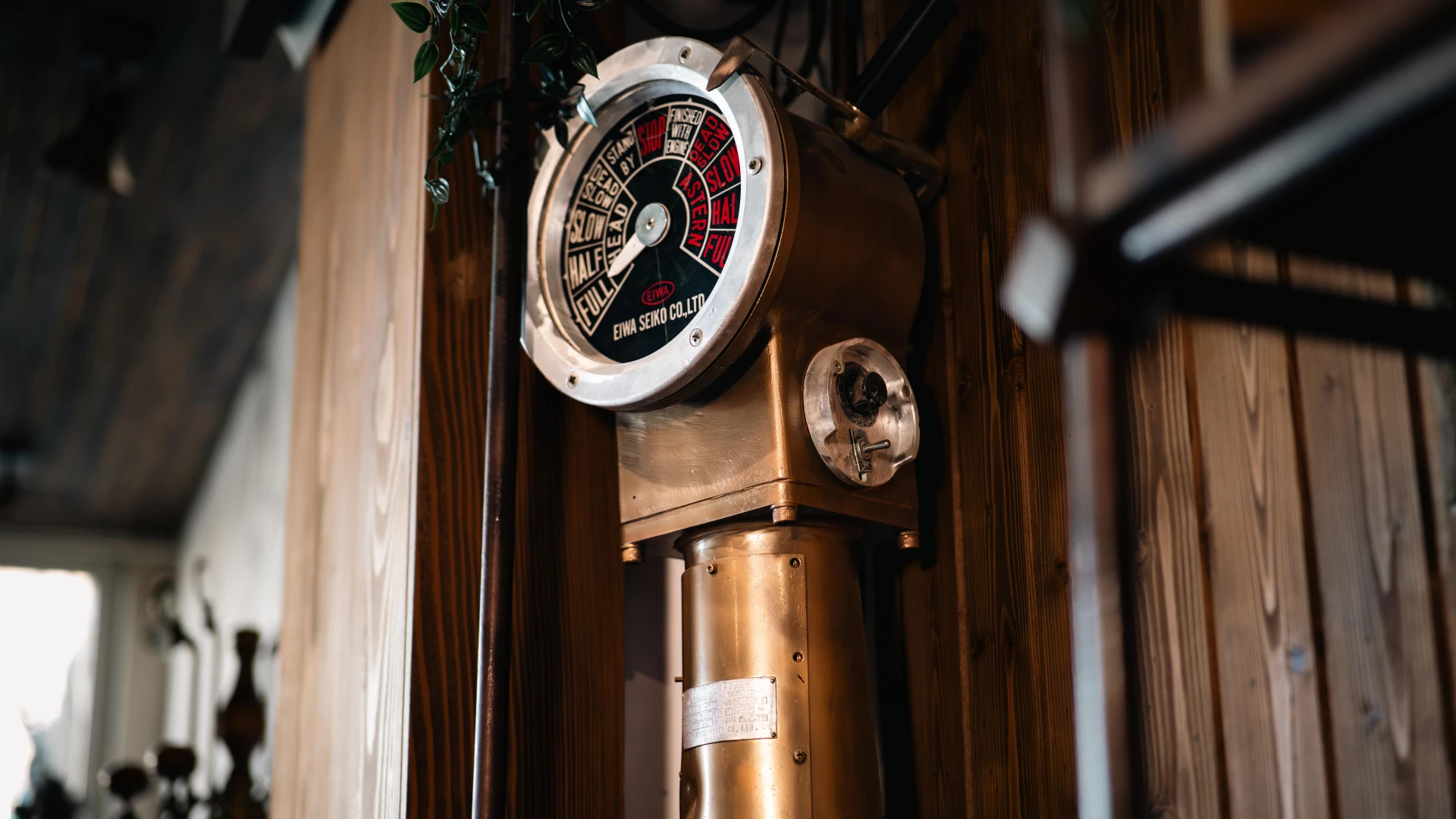
This manual engine order telegraph, built by Eiwa Seiko Co. Ltd., was used to transmit orders from the bridge to the engine room. A key component in traditional maritime navigation, this British model ensured precise control over ship operations before being replaced by modern electronic systems. With its durable design and mechanical precision, it played a crucial role in ship maneuvering and safety. Now displayed at Terasa cu Ancore, it remains a remarkable piece of maritime engineering.

This English stern/bow lantern, crafted from aged brass, was a crucial tool for ship illumination and signaling. Featuring a flame-protection system, it ensured optimal visibility in harsh maritime conditions. This well-preserved maritime artifact tells the story of British naval craftsmanship and its vital role in historical navigation.
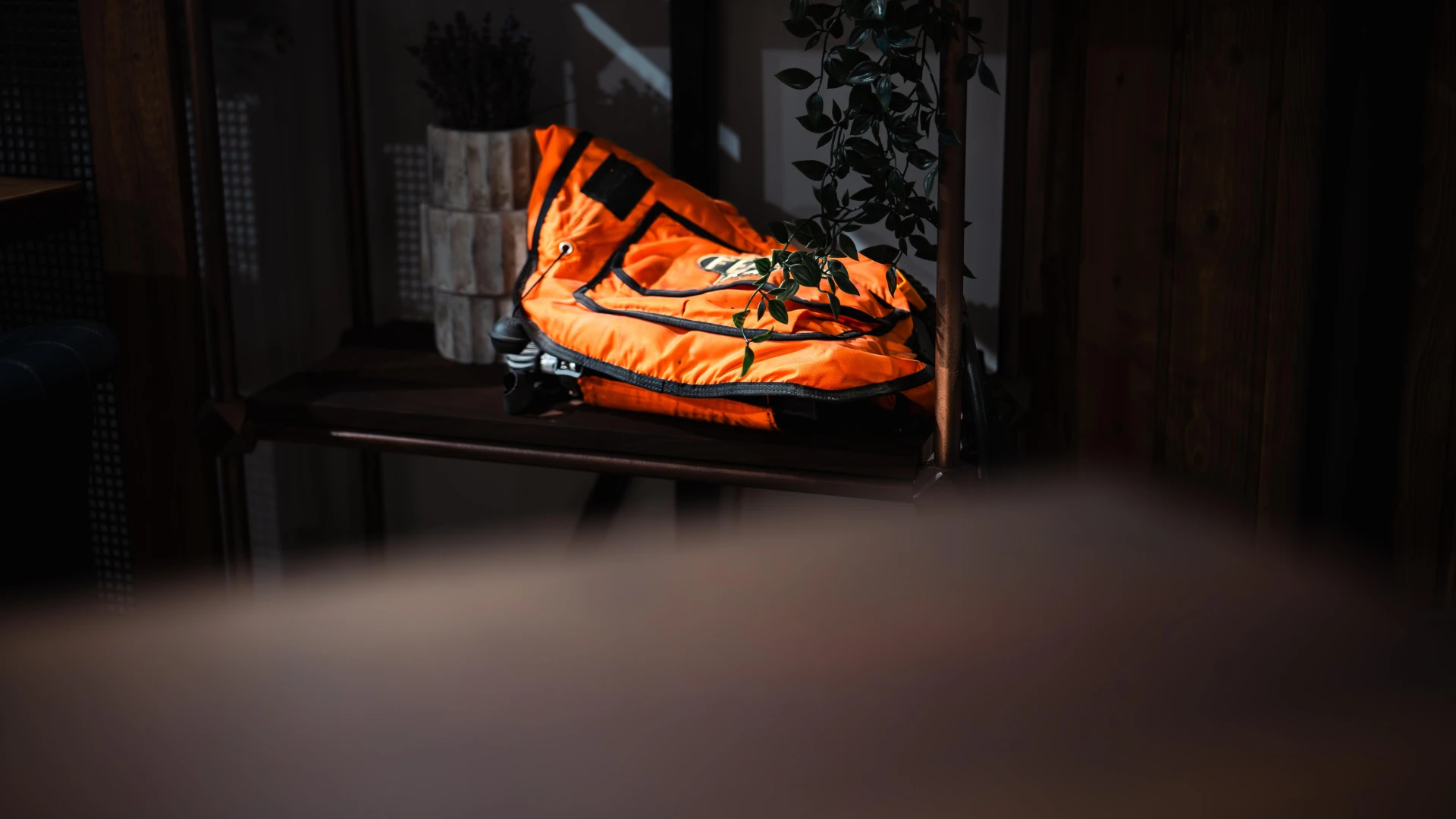
This Fenzy life vest is a crucial diving safety device, used for buoyancy control and surface stability. Designed with a quick inflation system, it provides security in challenging underwater conditions. Used in commercial and military diving, this vest is a key piece of subaquatic safety gear.

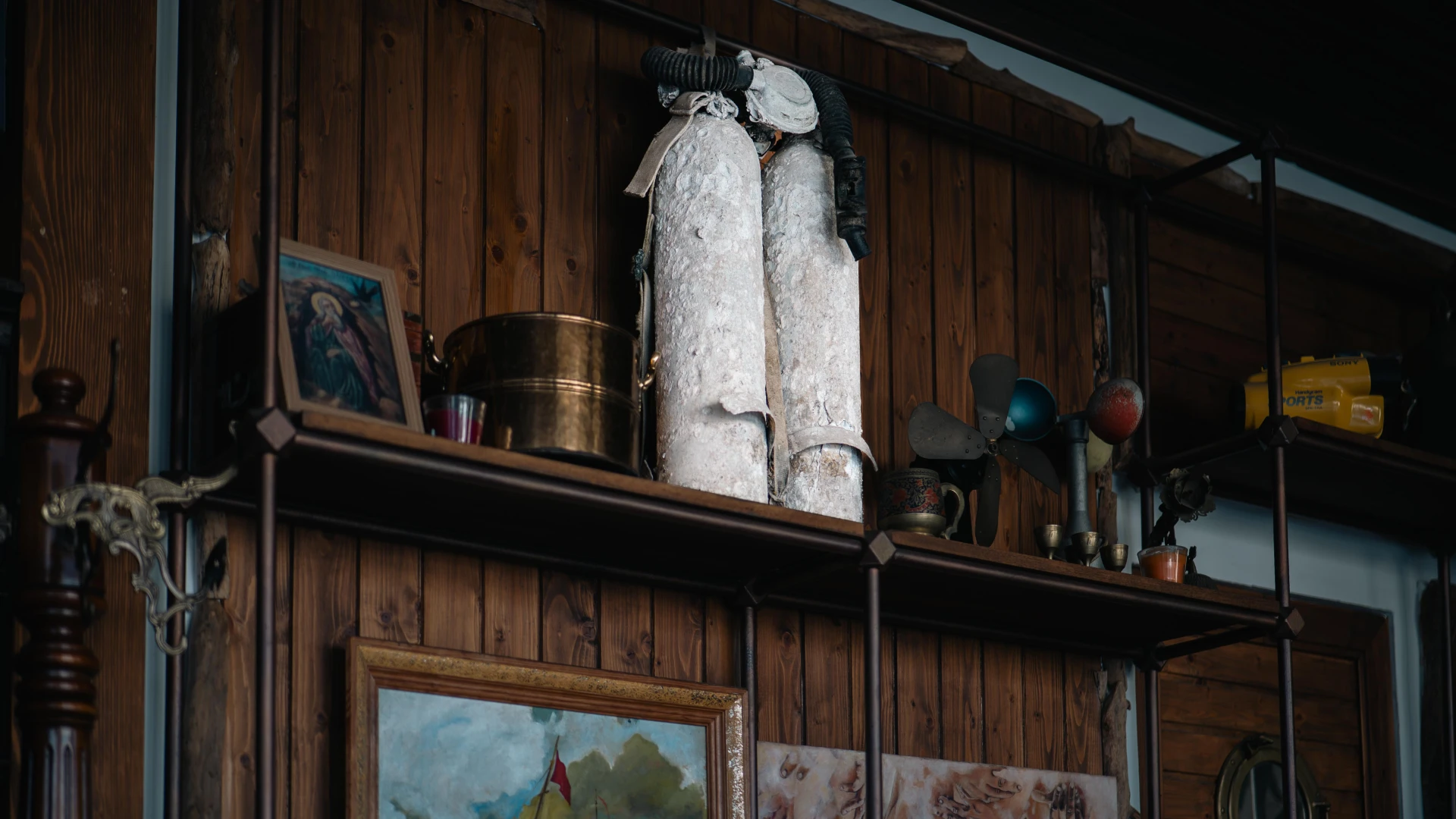
This aluminum double cylinder, equipped with a Mistral regulator, was part of the revolutionary diving equipment used by the legendary explorer Jacques-Yves Cousteau. Manufactured by Spirotechnique, this piece played a crucial role in shaping modern diving by providing divers with an optimized compressed air supply for underwater exploration. This particular unit was recovered from the Black Sea by military diver Haralambie Ștefan, serving as a rare testament to diving history and technological advancements. A remarkable artifact, now exhibited at Terasa cu Ancore.

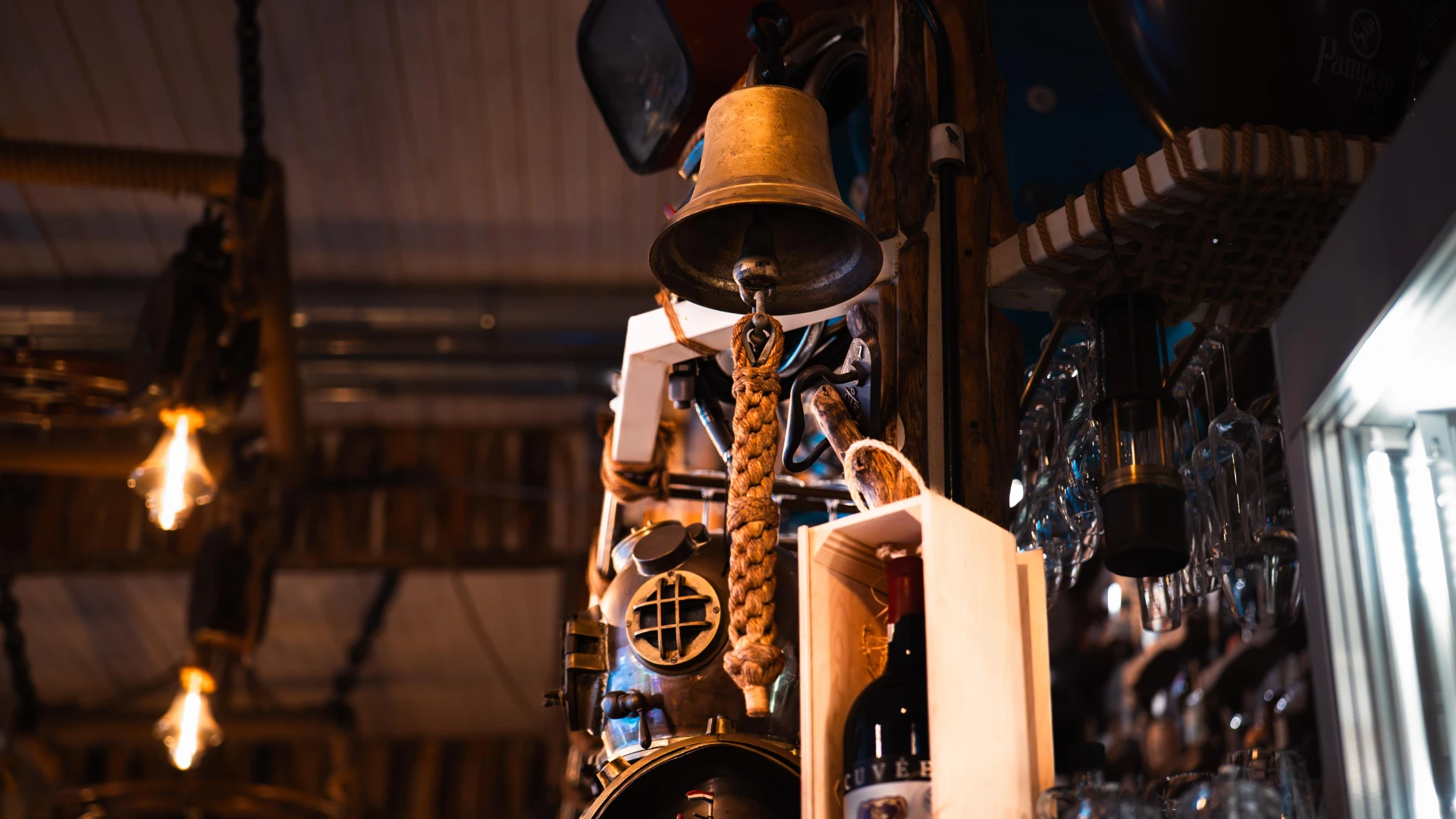
This ship bell played a crucial role in acoustic communication onboard, signaling dangers, watch shifts, and maneuvers. Recovered from a sunken vessel by the NemoProDiving team, it stands as a true symbol of seafaring history. Made of solid bronze, it has withstood the test of time, echoing the maritime past of sailors.

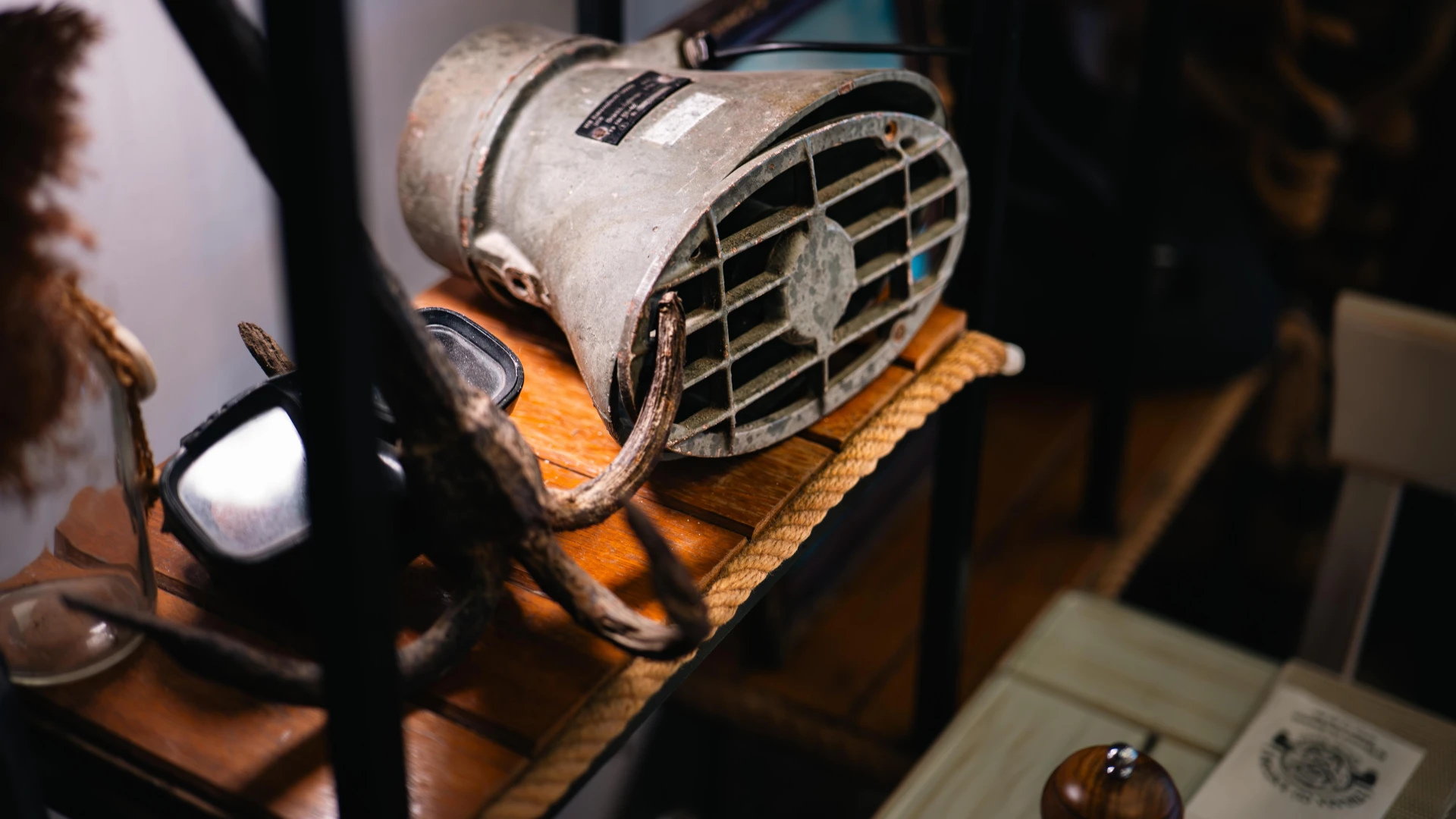
This naval speaker was part of traditional onboard communication systems, used on commercial and military vessels. Built to withstand harsh maritime conditions, it ensured clear message transmission among the crew. Its durable design highlights the importance of coordination and safety at sea, making it a crucial element of shipboard life. Now preserved at Terasa cu Ancore.

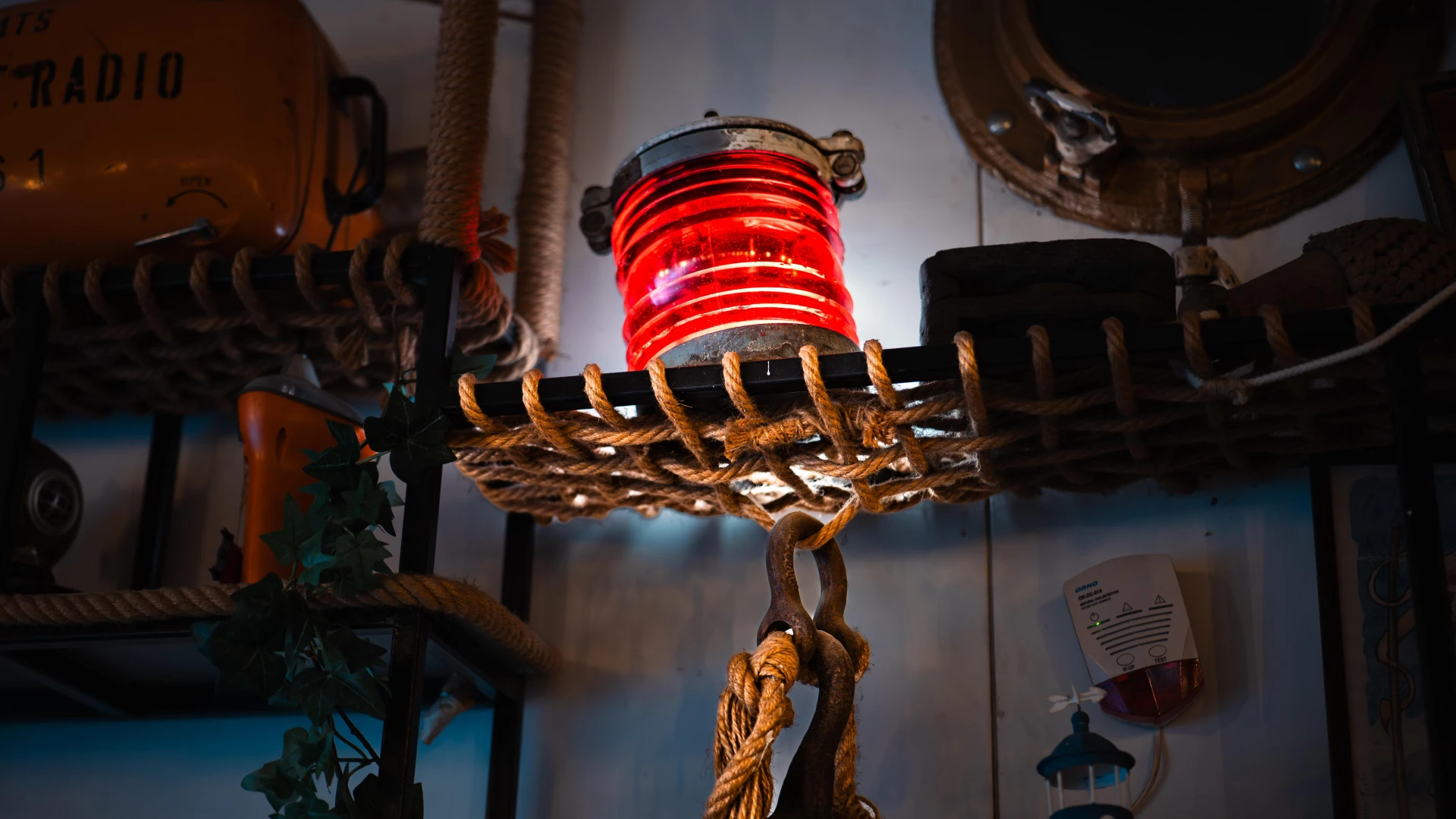
This red navigation light was used for indicating a vessel’s direction at night or in low visibility conditions. Placed on port or starboard, it played a critical role in collision prevention and compliance with international maritime regulations. Built with thick resistant glass and a durable metal casing, this light remains a symbol of safety and orientation at sea.

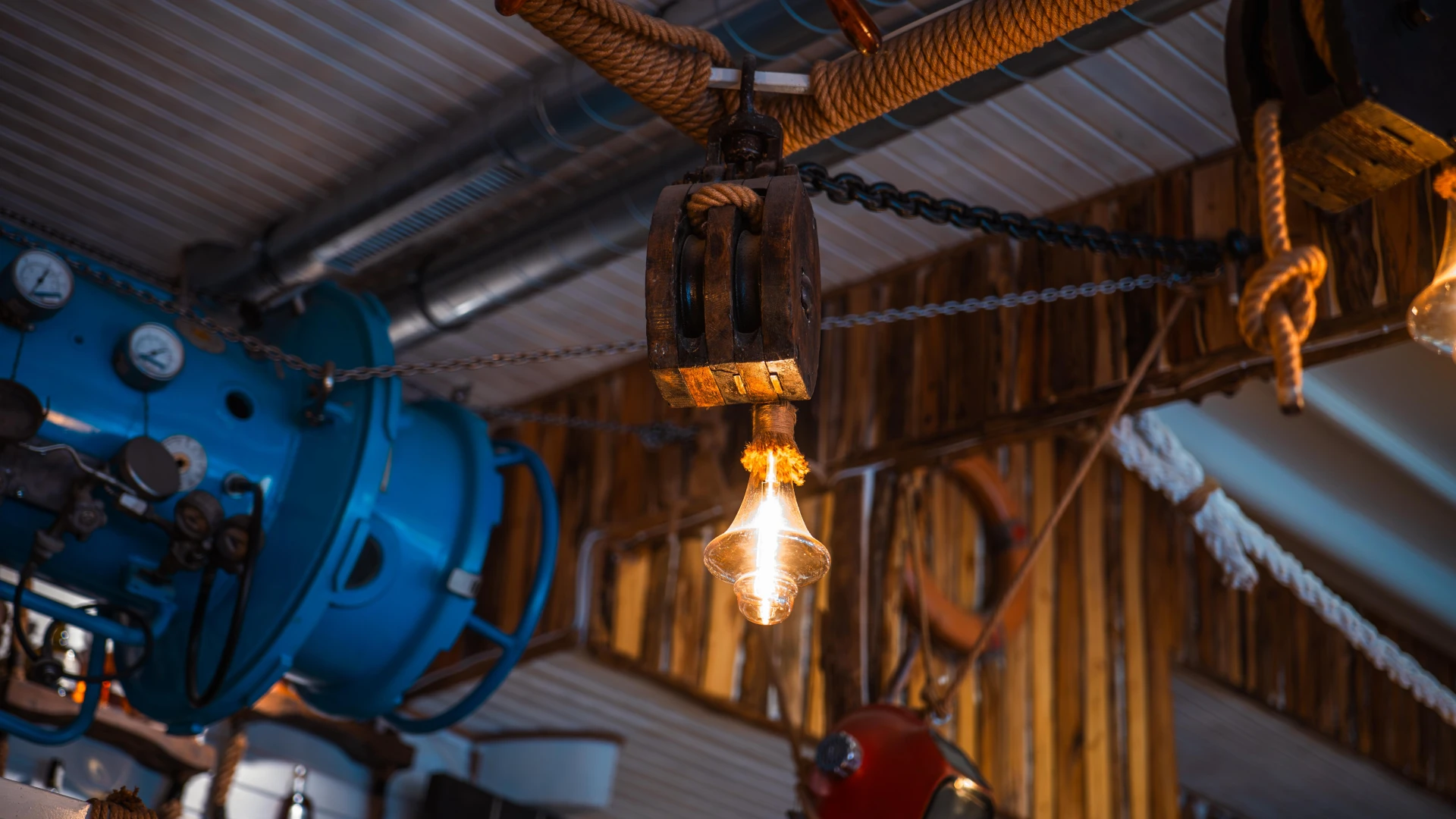
This wooden nautical pulley, over 200 years old, was an essential tool on sailing ships, used to hoist sails and lift heavy objects. Crafted from solid wood and metal, this robust mechanism was widely employed on merchant and military vessels, showcasing durability and efficiency in extreme maritime conditions. A true relic of traditional naval engineering.

This watertight maritime telephone was a crucial device for emergency communication on military and commercial ships. Built with a shockproof and waterproof metal casing, it was used on decks and in engine rooms, ensuring clear transmission of commands even in extreme conditions. Featuring a moisture-proof system, this robust model played a key role in secure onboard communications for decades.

This ship’s porthole, salvaged by the NemoProDiving commercial diving team, belonged to a sunken vessel. Made of solid bronze and pressure-resistant glass, it provided natural light and visibility inside the ship. Its watertight design ensured protection from water and harsh conditions, making it a crucial part of maritime engineering. A true nautical artifact, holding the stories of countless sailors who once gazed through it.
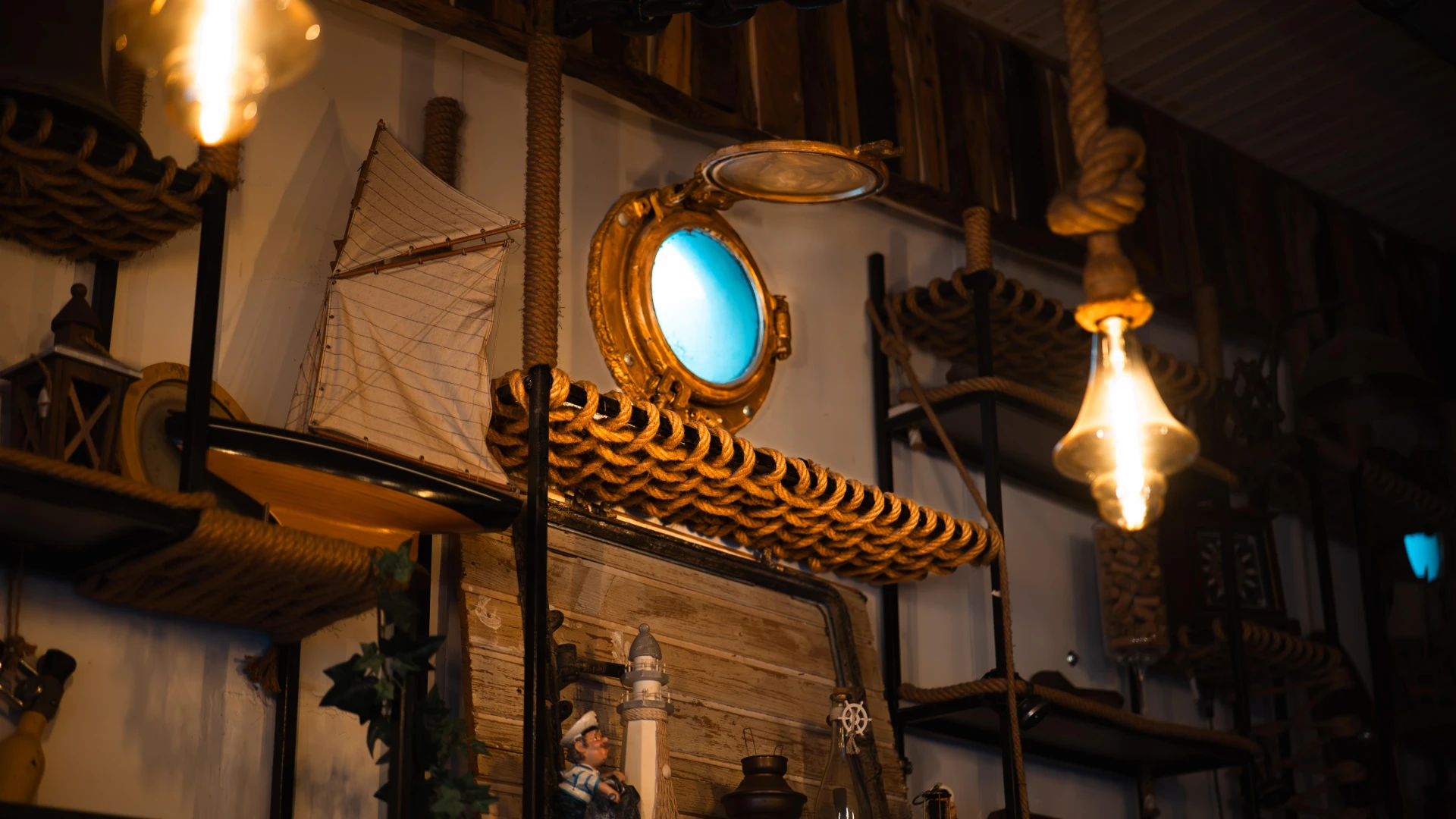

This Russian gas-powered compass, approximately 150 years old, is a masterpiece of maritime engineering. Designed for nighttime navigation, it used a gas illumination system, enabling sailors to maintain their course even in low visibility. Crafted from solid metal, with a durable and functional design, this rare artifact showcases the technological evolution of 19th-century navigation instruments.

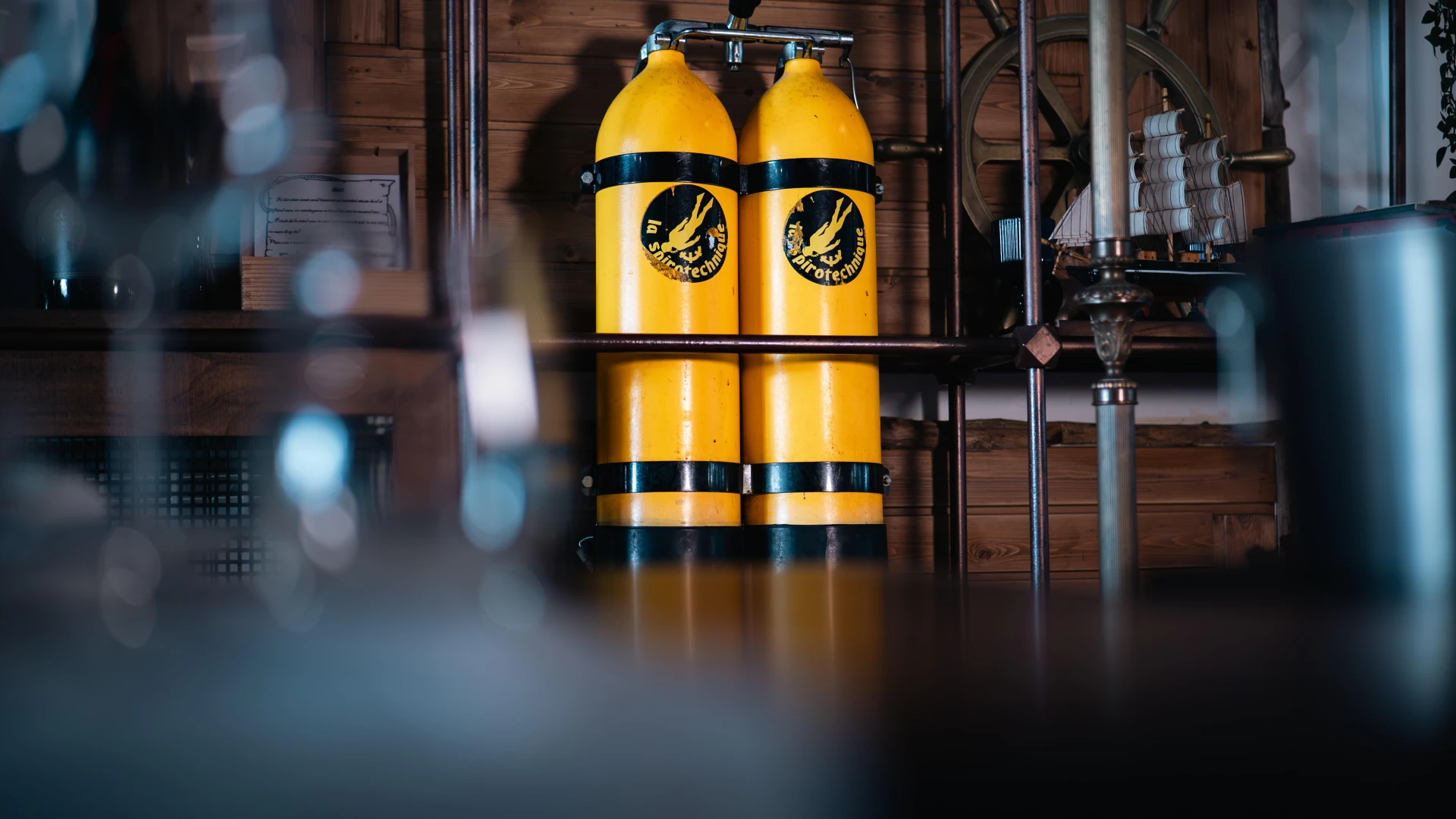
This French-made Spirotechnique bi-bouteille tank was designed for professional and military diving. Built for reliability and extended autonomy, it allowed divers to operate at greater depths with an optimal air supply. Featuring a sturdy design and balanced distribution system, this equipment set the standard in diving technology. Now displayed at Terasa cu Ancore, this rare piece showcases underwater exploration advancements.

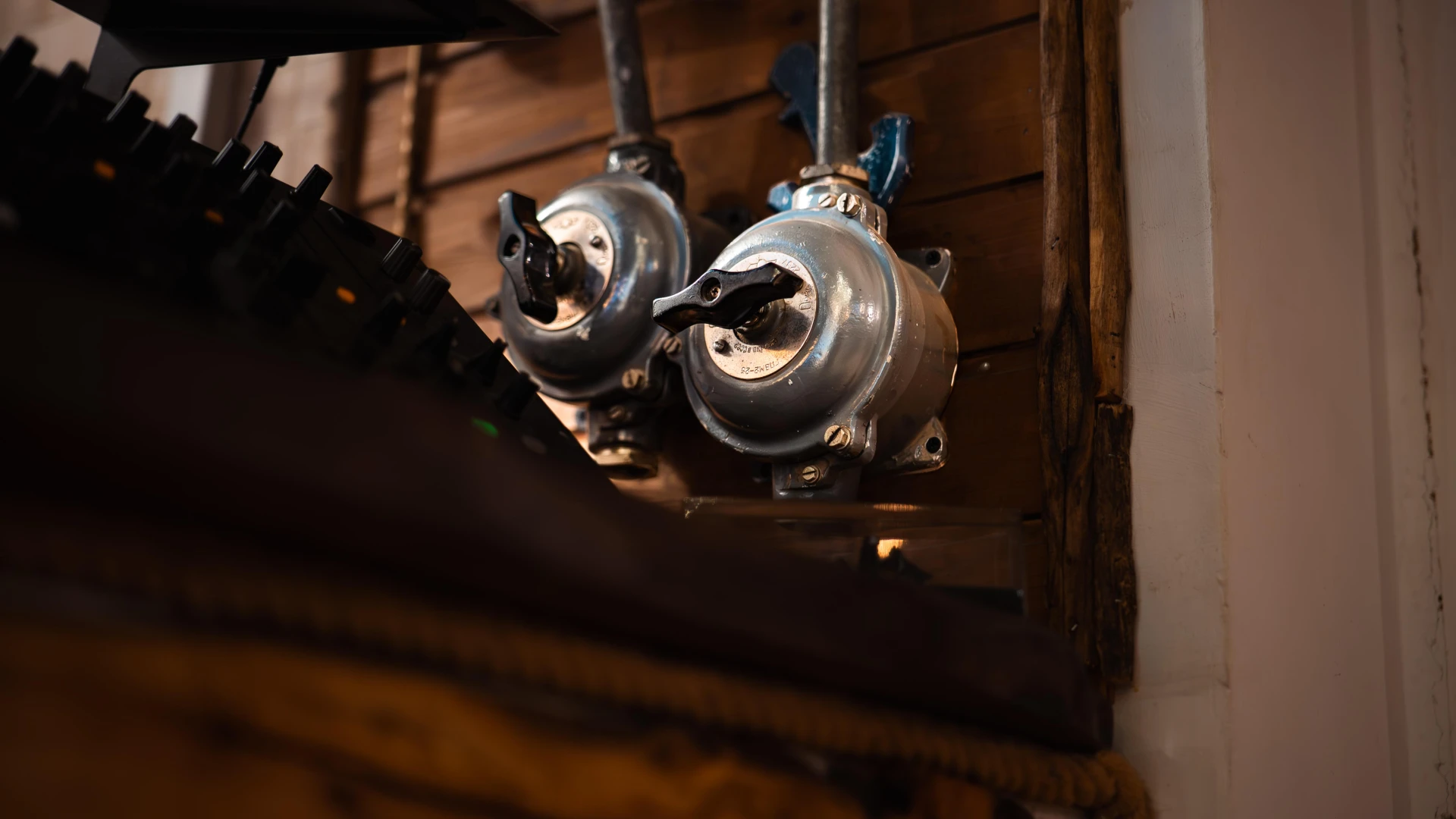
These authentic naval switches, once used on commercial ships, have been restored and repurposed for the Terasa cu Ancore bar. Fully functional and preserving their industrial aesthetic, these controls provide a tangible connection to maritime history. A unique detail that enhances the venue's nautical ambiance.

This La Spirotechnique helmet, a French prototype for deep-sea diving, operates with surface-supplied air and a helium-oxygen gas mix. Featuring a large, watertight visor, it provides optimal visibility in extreme underwater conditions. Used in technical and research diving, this rare piece marks a significant step in the evolution of deep-sea equipment.
